Discover the meaning of HMD in computer lingo. Explore its definition, types, components, applications, advantages, and disadvantages in this informative post.
Have you ever come across the acronym HMD while discussing computers or technology? It seems like the tech world is filled with abbreviations and acronyms that can leave you feeling quite perplexed. But fear not, because in this article, we will unravel the mystery of what HMD stands for in the realm of computers. From exploring its various meanings across different contexts to its significance in the virtual reality (VR) domain, we will shed light on this intriguing acronym. So, without further ado, let’s dive in and discover the true meaning of HMD in computer lingo.
HMD Stands for in Computer
Virtual reality (VR) technology has revolutionized the way we interact with computers, and one of the key components of the VR experience is the Head-Mounted Display (HMD). HMD is an abbreviation for Head-Mounted Display, a device that is worn on the head to provide a visual display to the user. In this article, we will explore the definition, history, types, components, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of HMDs in computer technology. We will also discuss the difference between HMDs and VR, highlight some popular HMDs in the market, and speculate on the future of HMDs in computer technology.

HMD Definition
HMD stands for Head-Mounted Display, which is a device worn on the user’s head to provide a visual display. It is a crucial component in virtual reality and augmented reality experiences, as it allows users to immerse themselves in a digital environment by providing a visual representation of that environment. HMDs typically consist of a display screen(s) that is positioned in front of the user’s eyes, along with other components such as sensors, lenses, and audio devices.
History of HMD in Computing
The concept of wearable displays can be traced back to the 1960s when Ivan Sutherland and Bob Sproull developed the first HMDs at Harvard University. These early HMDs were bulky and primarily used for military purposes, such as flight simulation or targeting systems. Over time, advancements in technology led to the development of more compact and affordable HMDs that were suitable for consumer use.

Types of HMDs in Computer
There are several types of HMDs available in the market, each offering unique features and applications. The two main categories of HMDs are virtual reality HMDs and augmented reality HMDs.
Virtual reality HMDs are designed to create a completely immersive virtual environment for users. They typically have a higher field of view (FOV) and use stereoscopic displays to provide a 3D effect. Examples of popular virtual reality HMDs include the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR.
Augmented reality HMDs, on the other hand, overlay digital information onto the real world, allowing users to interact with both virtual and physical elements. These HMDs often have transparent displays and incorporate sensors to track the user’s position and movement. The Microsoft HoloLens and the Magic Leap One are prominent examples of augmented reality HMDs.
Components of HMDs
HMDs consist of various components that work together to provide the immersive experience. These components include:
- Display: The display is the most crucial component of the HMD, as it determines the quality and clarity of the visual output. Most HMDs use OLED or LCD panels for their displays.
- Optics: HMDs utilize lenses to focus the display output and adjust the focal length, ensuring the user sees the virtual or augmented content in the correct perspective.
- Sensors: Sensors, such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers, are integrated into HMDs to track the user’s head movements and provide real-time data for a more immersive experience.
- Audio: HMDs often feature built-in speakers or audio jacks to provide spatial audio, further enhancing the immersive experience by simulating sound from different directions.
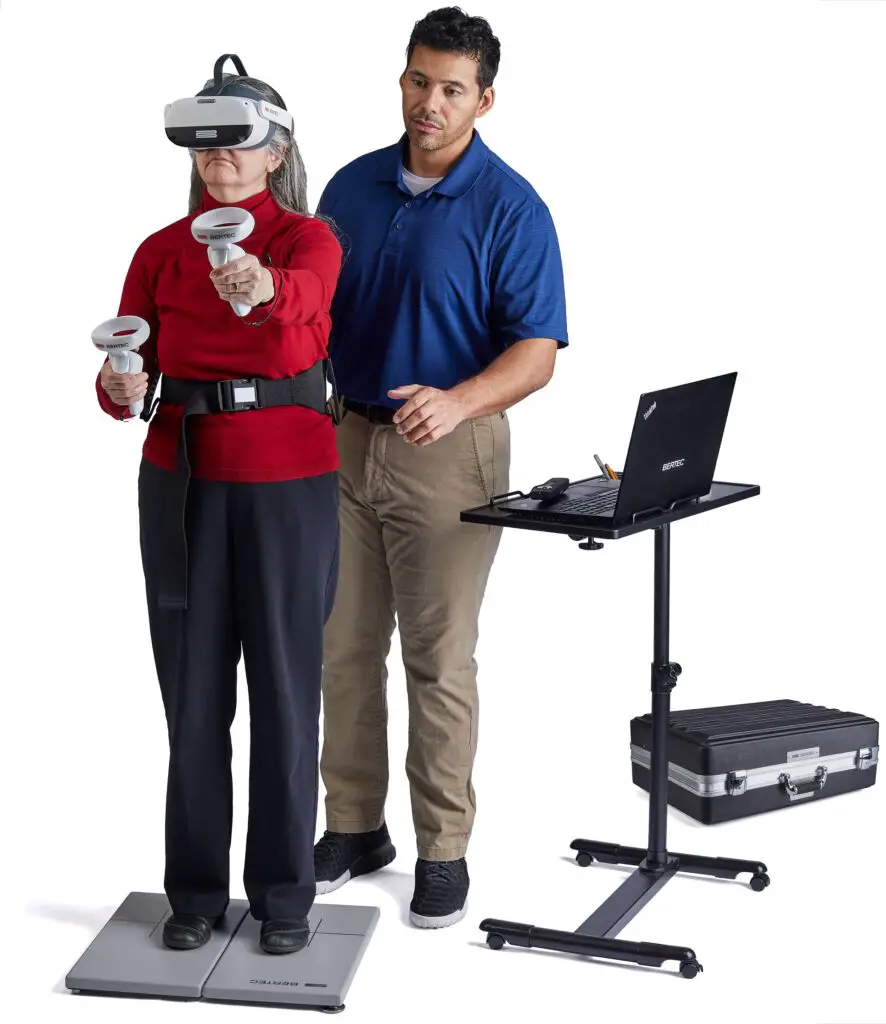

Applications of HMDs in Computer
HMDs have a wide range of applications in computer technology, spanning various industries and fields. Some of the notable applications of HMDs include:
- Gaming and Entertainment: HMDs have revolutionized the gaming industry by providing an unparalleled level of immersion. Gamers can now step into virtual worlds and interact with the game environment like never before.
- Training and Simulation: HMDs are extensively used in training and simulation applications, such as flight simulators, medical training, and military simulations. They allow trainees to practice in realistic virtual environments, reducing the risks and costs associated with real-world training scenarios.
- Education: HMDs have the potential to transform the education sector by providing immersive learning experiences. Students can explore historical landmarks, dive into the depths of the ocean, or even interact with virtual models of complex concepts.
- Design and Visualization: HMDs are valuable tools for designers, architects, and engineers as they enable them to visualize and evaluate their creations in virtual or augmented environments. This allows for better design iterations and enhances the overall design process.
Advantages of HMDs in Computer
HMDs offer several advantages in computer technology. Some of the key advantages include:
- Immersive Experience: HMDs provide a level of immersion that is unmatched by other display technologies. By wearing the HMD, you are transported into a digital world, increasing the sense of presence and engagement.
- Hands-Free Interaction: With HMDs, you can interact with the virtual or augmented content using natural gestures or voice commands, eliminating the need for traditional input devices such as keyboards or controllers.
- Realistic Training Simulations: HMDs enable realistic training simulations, allowing trainees to practice in safe and controlled virtual environments. This can be particularly useful in high-risk industries such as medicine, aviation, and manufacturing.
- Enhanced Visualization: HMDs provide a unique way to visualize complex data or designs. By immersing yourself in the virtual environment, you can gain a better understanding of spatial relationships and make more informed decisions.
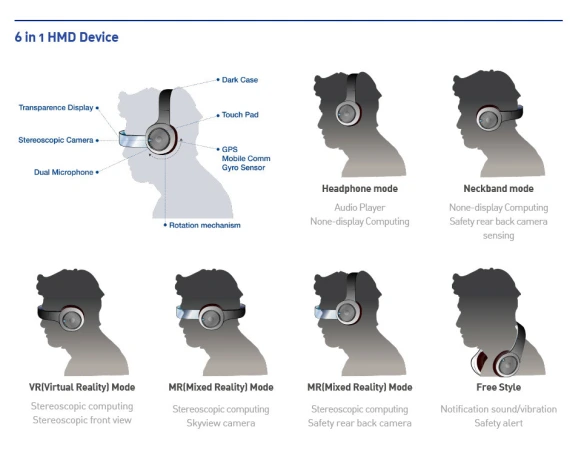
Disadvantages of HMDs in Computer
Despite their numerous advantages, HMDs also have certain drawbacks that need to be considered. Some of the main disadvantages include:
- Cost: HMDs can be expensive, especially high-end devices that offer advanced features. This can limit their accessibility to a broader audience, particularly for applications beyond gaming.
- Motion Sickness: Sustained use of HMDs can cause motion sickness for some individuals. The combination of visual stimuli and lack of physical movement synchronization can lead to discomfort or disorientation.
- Limited Field of View: While HMDs have significantly improved over the years, they still have limitations in terms of the field of view. Users may experience a tunnel vision effect, which can reduce the overall immersion.
- Social Isolation: HMDs, by their very nature, tend to isolate the user from their physical surroundings. This can lead to a lack of social interaction and inhibit collaboration in certain environments.
HMD vs VR: Understanding the Difference
It is important to clarify the difference between HMD and VR, as they are often used interchangeably. HMD refers to the physical device that the user wears on their head, whereas VR stands for virtual reality, which is the digital environment created by the HMD. In other words, HMD is the hardware component, and VR is the software or content that is displayed through the HMD.
Think of the HMD as the window through which you view the virtual reality world. It provides the means for you to see and interact with the digital environment, while VR encompasses the entire experience, including visuals, audio, and interactivity.

Popular HMDs in Computer
The HMD market is continuously evolving, with new devices being introduced regularly. Some of the popular HMDs in the computer realm include:
- Oculus Rift: Developed by Oculus VR, a subsidiary of Facebook, the Oculus Rift is widely regarded as one of the pioneers of modern virtual reality HMDs. It offers a high-quality VR experience with advanced features such as positional tracking and hand controllers.
- HTC Vive: Created in collaboration with Valve Corporation, the HTC Vive offers a room-scale VR experience, allowing users to physically move within the virtual environment. It features precise tracking and a wide variety of compatible games and applications.
- Microsoft HoloLens: While not strictly a VR HMD, the Microsoft HoloLens is a leading augmented reality device. It uses transparent displays to overlay 3D holograms onto the real world, enabling users to interact with virtual objects seamlessly.
Future of HMDs in Computer
The future of HMDs in computer technology looks promising as advancements in hardware, software, and connectivity continue to push the boundaries of what is possible. Some of the anticipated developments include:
- Increased Display Resolution: Improvements in display technology will likely lead to higher resolutions and pixel densities, enhancing the visual quality of HMDs.
- Wireless Connectivity: Wireless HMDs are becoming more prevalent, offering greater freedom of movement and eliminating the need for cables. This trend is expected to continue as wireless technologies improve.
- Eye-Tracking Technology: Eye-tracking is a developing area in HMDs, allowing for more natural interactions. Future HMDs may incorporate eye-tracking to enable more intuitive control and enhance the overall user experience.
- Enhanced AI Integration: Artificial intelligence (AI) can play a significant role in improving the user experience by adapting content and interactions based on user preferences and behaviors. Expect HMDs to incorporate AI capabilities for a more personalized and immersive experience.
In conclusion, HMDs have revolutionized the computer industry by providing immersive virtual and augmented reality experiences. From gaming and entertainment to training and education, HMDs have found applications in various fields. While they offer numerous advantages such as an immersive experience and enhanced visualization, there are also challenges to overcome, such as cost and motion sickness. The future of HMDs looks promising, with advancements in display resolution, wireless connectivity, eye-tracking, and AI integration paving the way for even more immersive and interactive experiences.
